A stroke can happen to anyone at any age. According to the American Stroke Association, someone in the United Sates has a stroke every 40 seconds.
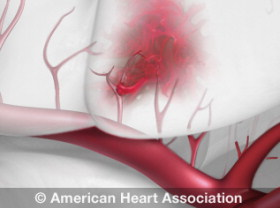
So how do strokes strike? Strokes occur when there is bleeding in the brain or when there is a blockage resulting in blood and oxygen not flowing to the brain. A stroke limits the oxygen supply to the brain and can lead to serious brain damage.
Every minute a stroke goes untreated, a person loses about 1.9 million neurons, which can affect speech, memory, movement and so much more. Learn to spot a stroke fast by knowing the signs to look out for. The warning signs include:
Signs of Stroke
- Numbness or weakness of face, arm or leg, especially in one side of the body
- Sudden severe head pain
- Difficulty speaking or understanding language
- Unexplained dizziness, loss of balance
- Loss of vision or difficulty seeing in one or both eyes
Stroke Risk Factors
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Diet
- Lack of physical activity
- Diabetes
- Smoking
Three major types of stroke:
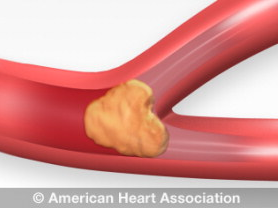
Ischemic Stroke
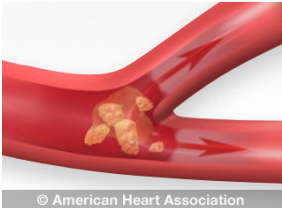
An ischemic stroke, also referred to as a clot, occurs when there is a blockage in the blood vessel as it supplies blood to the brain. This build-up is the result of fatty deposits lining the walls of the vessel. Fatty deposits can cause two types of blockage:
Cerebral thrombosis: a blood clot in the vessel
Cerebral embolism: a blood clot in another part of the circulatory system such as the heart or large arteries in the neck or chest. A piece of the clot detaches and enters blood stream until it reaches small vessels that won’t allow it to pass.
85% percent of stroke cases are caused by ischemic stroke.